|
With home prices at record high levels and mortgage rates at their record highs since the turn of this century, it’s natural to ask if the housing market will be the source of new systemic risk. Over the past year, we have written extensively about “mortgage winter”, a condition where housing demand is held back because of affordability, while at the same time, supply is constrained by current homeowners who are locked into properties by mortgages with rates far below those available in the prevailing market. This is what economists would call a “bad equilibrium”, a state of great strains in the market that tends to persist.
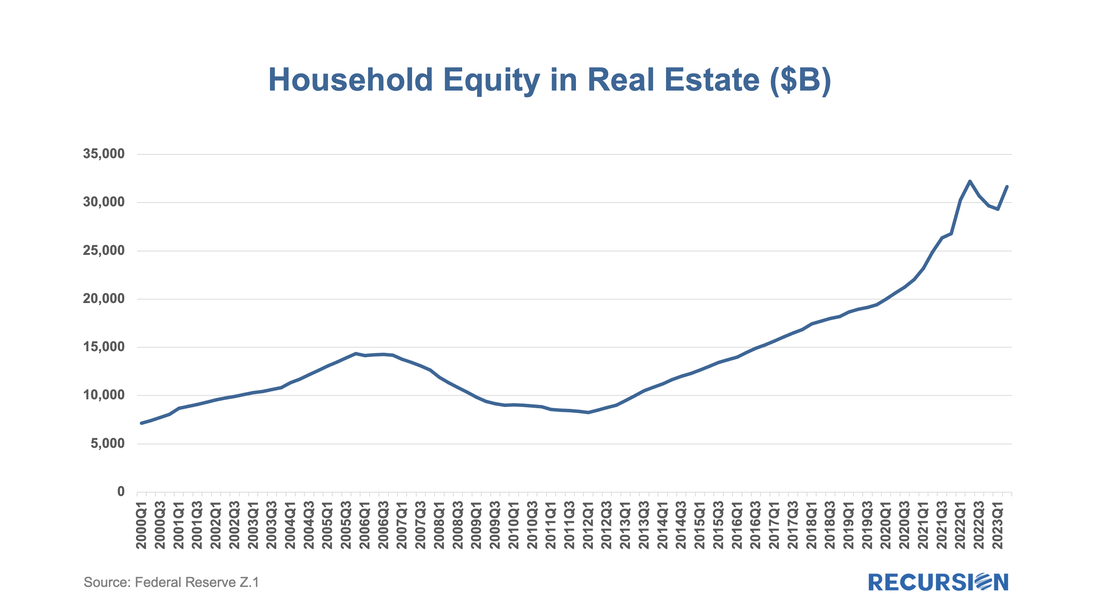
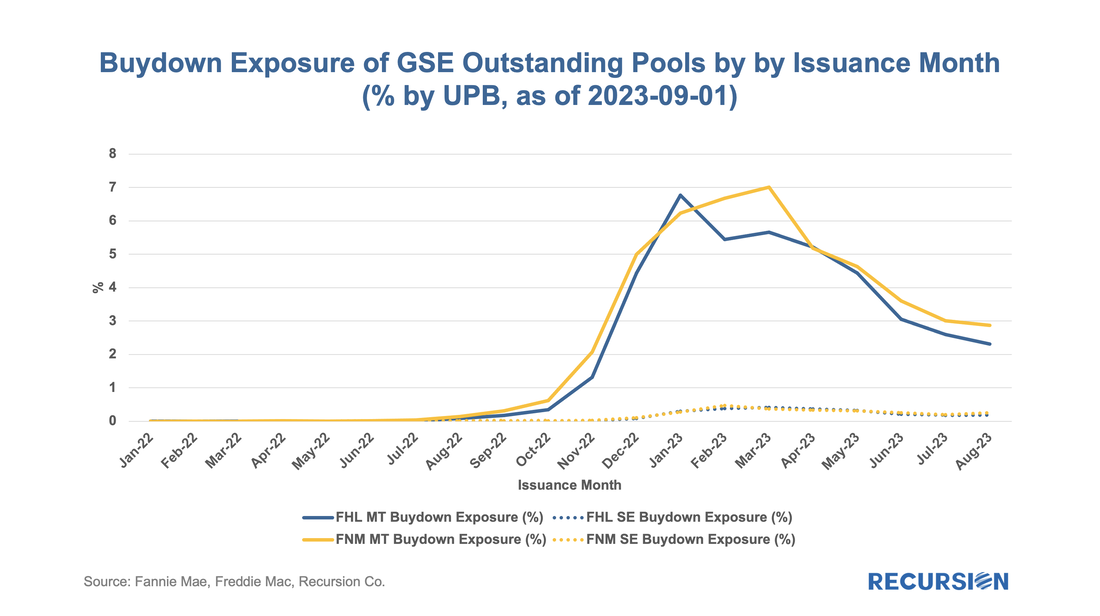
While the housing finance industry is under great duress, the spillover to the broader economy remains limited, as for example, the labor market has held up well despite soaring borrowing costs. Within housing, the notable good economic news is that the extraordinary surge in house prices in the wake of the Covid-19 pandemic has resulted in an astounding 50% surge in the value of homeowner’s equity in real estate since Q1 2020 to over $30 trillion. On June 29, 2023, both Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac announced enhancements to their MBS disclosures starting with the September monthly release[1]. The data covers active pools issued back to January 2022. As rates were quite low prior to this time, these disclosures cover the relevant period of high demand for buydowns:
In a recent post, we discussed trends in commercial real estate outstanding debt, with an emphasis on the Agency multifamily market[1]. We mentioned that the key difference between risk sources associated with multi- and single-family debt is that the I/O structure and balloon term that predominates in multifamily loans implies that there is significant refinance risk in this market.
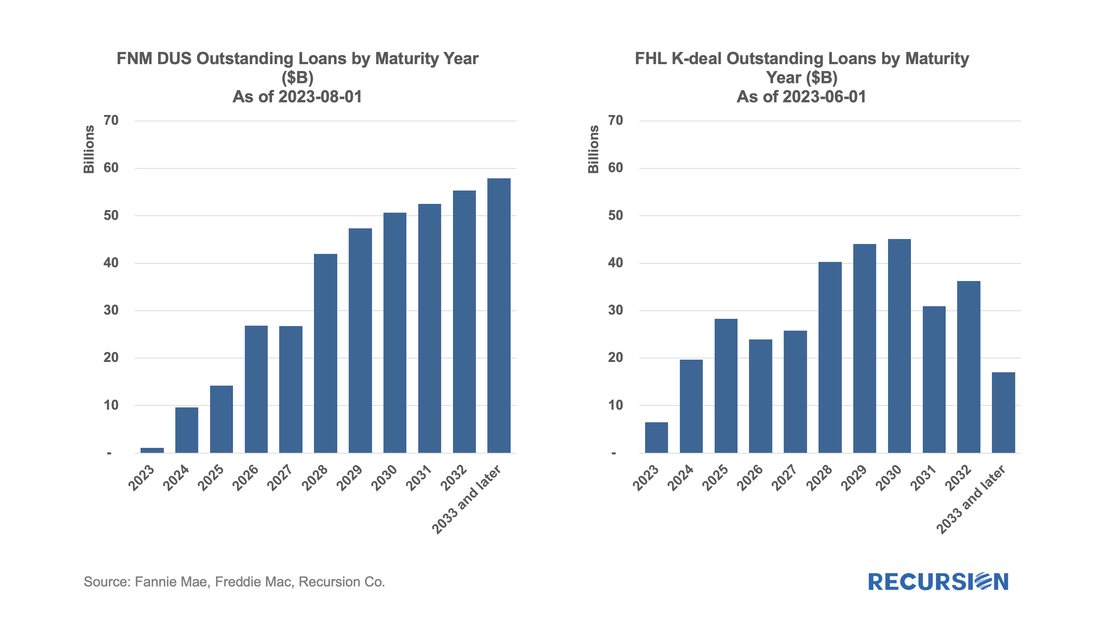
We also previously wrote that we have collected all the loans in the major Agency multifamily books and verified that this data was consistent with the Federal Reserve’s Z.1 report[2]. We are now prepared to take some first steps at estimating the extent of this risk. To simplify things, in this note, we look just at the two major GSE multifamily programs, Freddie Mae DUS[3] and Freddie Mac K-deals[4]. To begin, as of August 1, 2023, the Fannie Mae DUS deals account for $384.5 bn or 86% of the total FNM book of $448.1 bn, while Freddie K deals account for $317.9 bn or 83% of $384.9 bn outstanding as of June 1, 2023. Superficially similar. Below find the maturities for the two programs by year starting in June 2023 for Freddie Mac and August 2023 for Fannie Mae[5]: |
Archives
July 2024
Tags
All
|
RECURSION |
|
Copyright © 2022 Recursion, Co. All rights reserved.

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
