|
The recent release of “Social Scores” on the part of the GSE’s serves to point out the broad range of ESG issues facing the mortgage market.[1] Of course, this covers a lot of policy territory, and over time investors, lenders and policymakers will have to come to grips with the details associated with these concerns. In today’s post, we look at environmental issues related to the condo market.
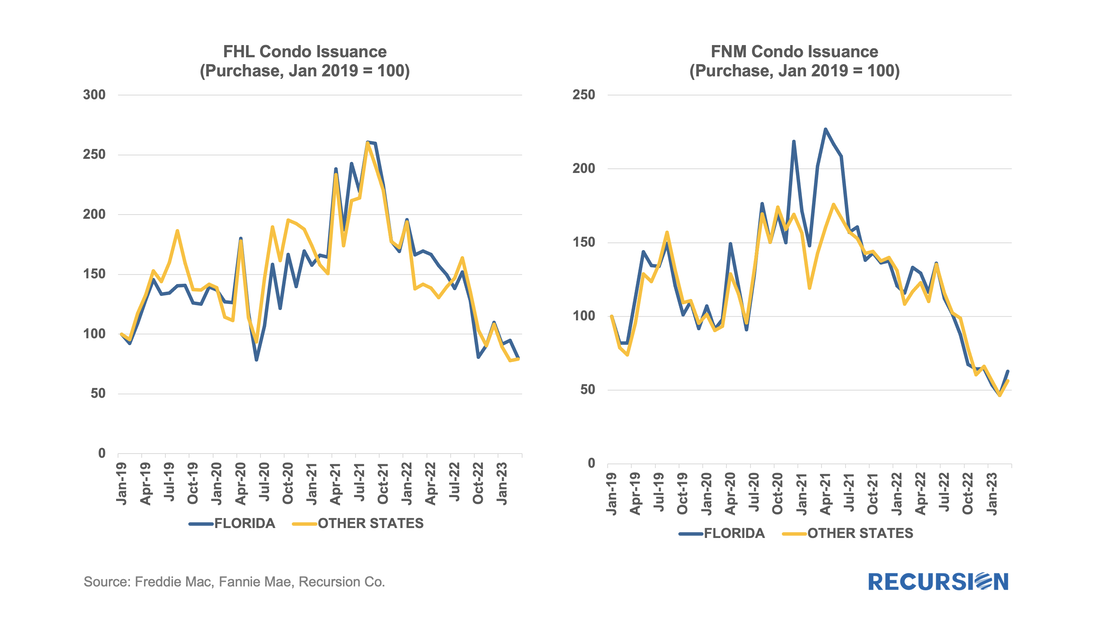
These issues came to a head with the disaster in Surfside Florida in June 2021, when the partial collapse of Champlain Towers South, a 12-story condo, resulted in 98 deaths and over $1 billion being awarded to victims in a class action lawsuit. Implications for regulation and insurance costs continue to be felt as the event brought home the immediacy of issues surrounding climate change to the general public. In October 2021, Fannie Mae issued a Lender Letter presenting tightened requirements that impact the eligibility of loans made in buildings with five or more attached units[2]. These new policies were “designed to support the ongoing viability of condo and co-op projects…(as) aging infrastructure and significant deferred maintenance are a growing concern across the nation.” These new standards came into effect on January 1, 2022. Among other things, they may land a building on an “unavailable” status if there is significant deferred maintenance, failure to pass local regulatory inspections, or not meeting the 10% budget reserve requirement. To see if there is any impact, we start with a look at Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae condo loan deliveries from January 2019 to March 2023. During this period, the two Enterprises delivered 1.16 million purchase loans securitized by a condo, of which Fannie Mae generally had a share of about 57%: Since the end of last year, the Government Sponsored Enterprises have released so-called “Social Score” Indexes that are made to appeal to ESG investors. Both Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac produce scores at the pool level based on a variety of social metrics. The following methodology summary comes from Fannie Mae[1] (Freddie Mac has adopted the same methodology as Fannie Mae’s):
In a previous note, we looked at mortgage trends derived from the recent release of 2022 HMDA data[1]. Of course, HMDA is a prime data source for analysts and policymakers who seek to understand how social and economic trends interact. The most discussed issue is the distribution of originations by race. Below find a bar chart for the share of originations by race annually from 2004-2022 by loan count:
|
Archives
July 2024
Tags
All
|
RECURSION |
|
Copyright © 2022 Recursion, Co. All rights reserved.

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
